Setting Workspace
Table of contents
This article is a document from AWS Workshop studio that has been practiced and monitored.
AWS Cloud9 is a cloud-based integrated development environment (IDE) that allows developers to write, run, and debug code from a web browser. It supports a variety of programming languages and can be used to develop various applications, including serverless, web, and mobile applications. Developers can use Cloud9 for code writing, debugging, testing, and deployment.
Cloud9 is integrated with other AWS services such as AWS Lambda, Amazon EC2, and AWS CodeStar, enabling developers to build and deploy applications. It also integrates with collaboration tools such as GitHub and Bitbucket to manage team projects.
As a browser-based IDE, developers can use Cloud9 without installing any software on their local computers. It is cloud-based, so developers do not need to install or maintain software on their computers. They can also leverage AWS security and management features.
AWS cloud9
IDE configuration with AWS Cloud9
Service > Cloud9
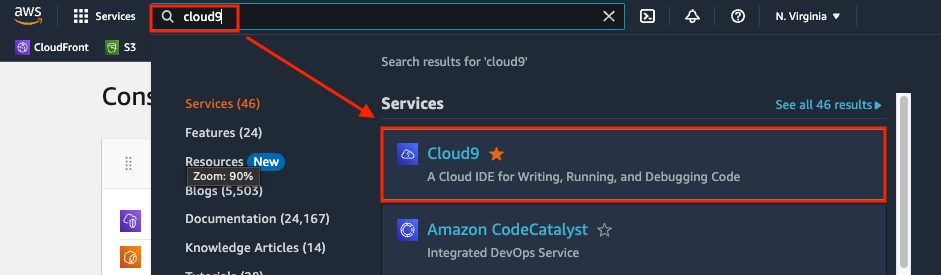
Click Create environment on the AWS cloud9 page

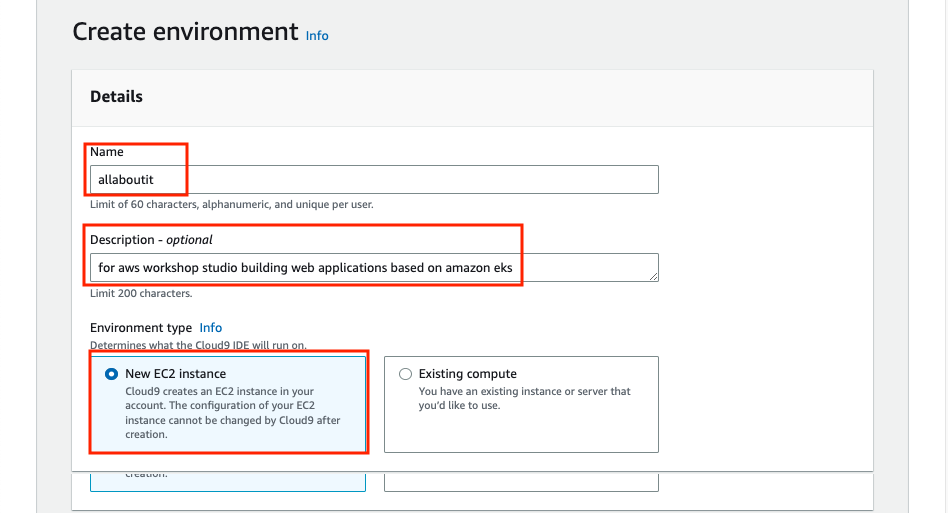
Put IDE name in blank box and put description in blank box too. and select New EC2 instance at Environment type.
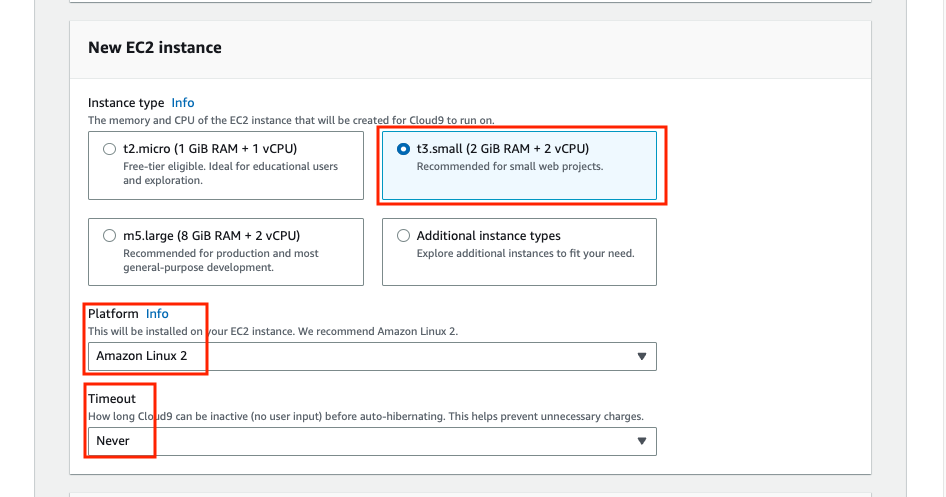
Select t3.medium in instance type at New EC2 instance and select Amazon Linux(recommended) in Platform. and select ‘Never’
Create IAM Role
Service > IAM > Roles > Create role
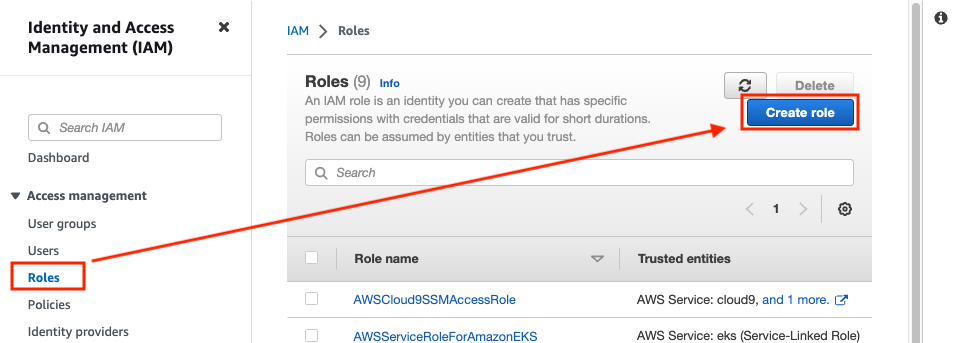
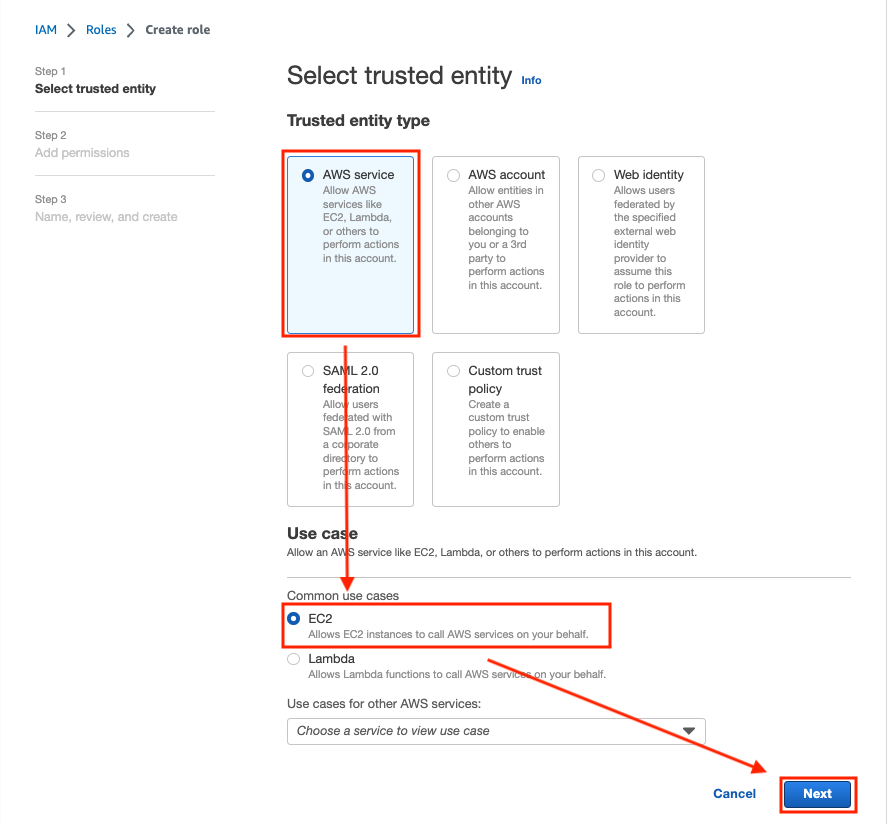
Check that AWS service and EC2 are selected click Next: Permissions
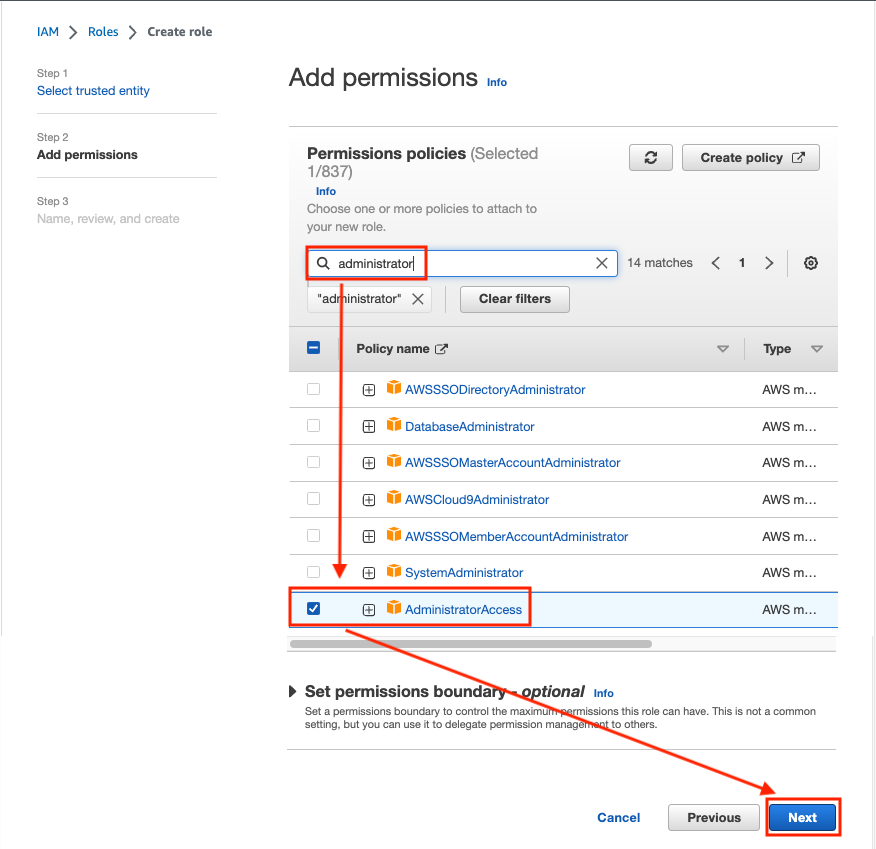
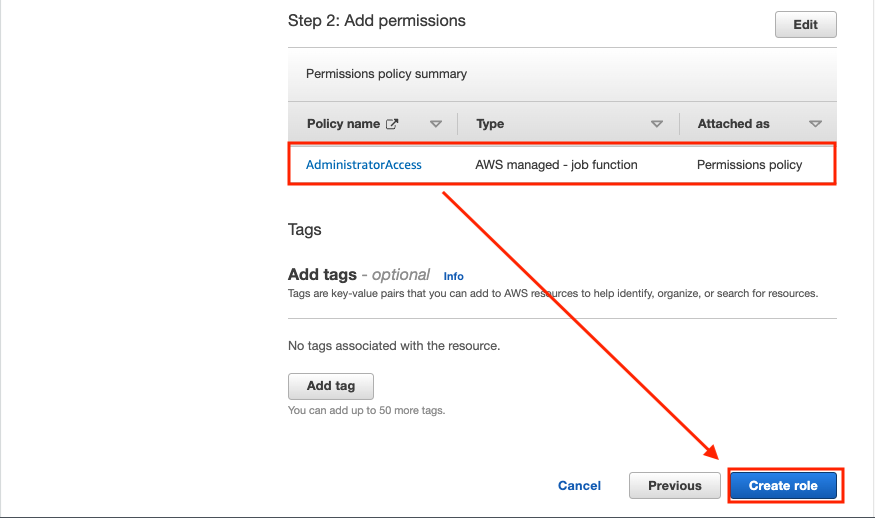
Check that the AdministratorAccess policy is selected and click Next: Name, review, and create.
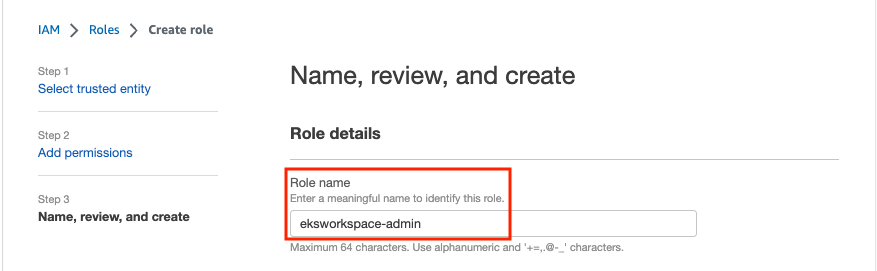
In Role name, type eksworkspace-admin, check that the AdministratorAccess selected policy has been added, and click Create role.
Grant AIM Role to an AWS Cloud9 Instance
The AWS Cloud9 environment is powered by an EC2 instance. Therefore, grant the IAM Role that you just created to the AWS Cloud9 instance in EC2 console.
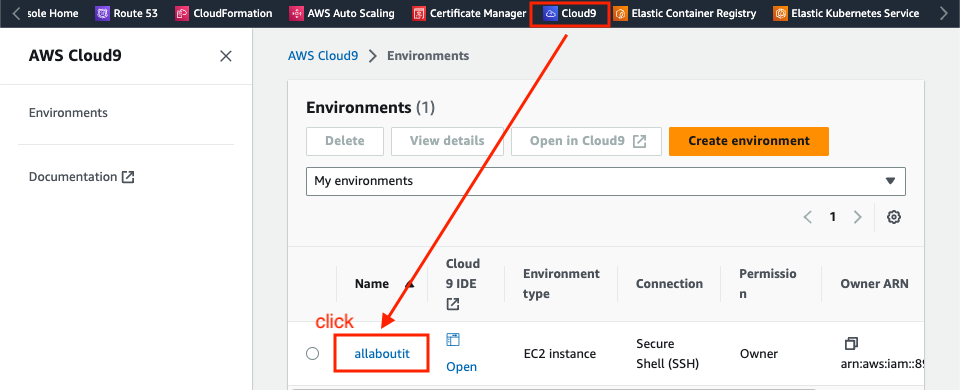
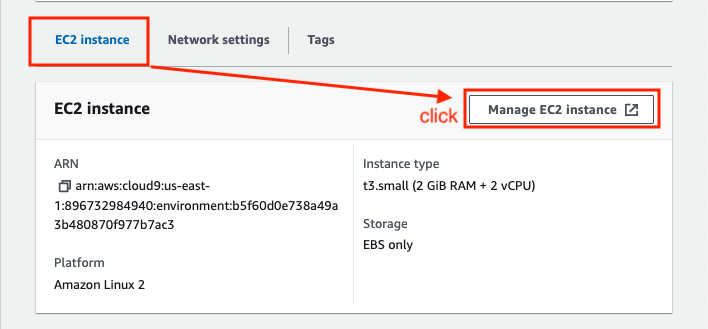
Cloud9 > [Environments name] > EC2 instance > Manage EC2 Instance
Click cloud9 instance name on the EC2 Instances’s list
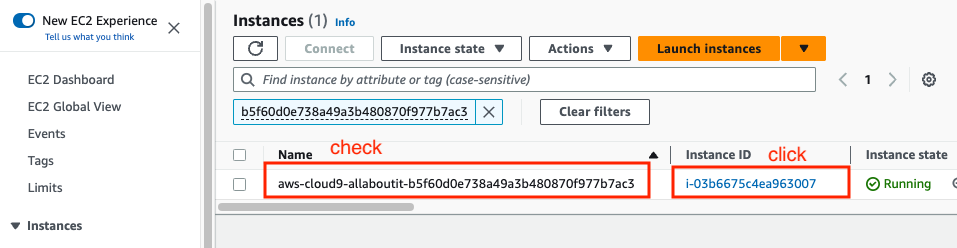
Click Actions > Security > Modify IAM Role.
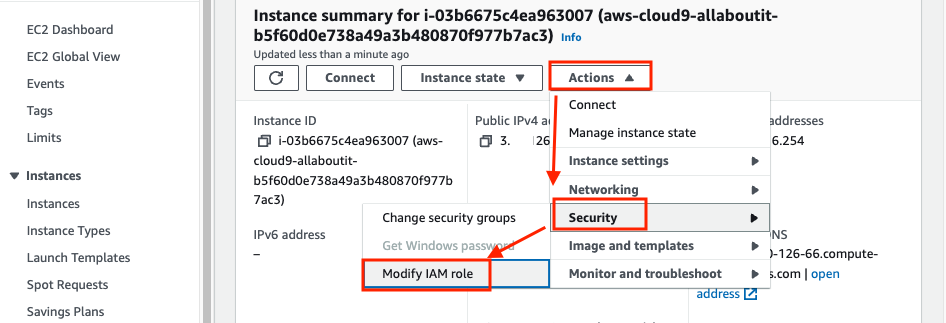
Select eksworkspace-admin in IAM Role section, then click the Update IAM role button.
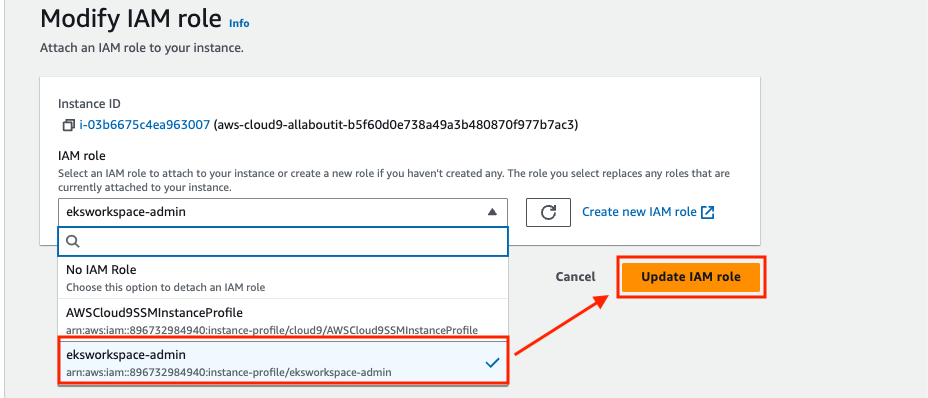
Update UAM settings in IDE
In AWS Cloud9, it dynamically manage IAM credits. Disable these credentials because they are not compatible with EKS IAM authentication. After that attach the IAM Role.
- Reconnect to the IDE you created in AWS Cloud9 console, click the gear icon in the upper right corner, and click AWS SETTINGS in the sidebar.
- Disable the AWS managed temperature credits setting in the Credentials topic.
Exit Preference tab.
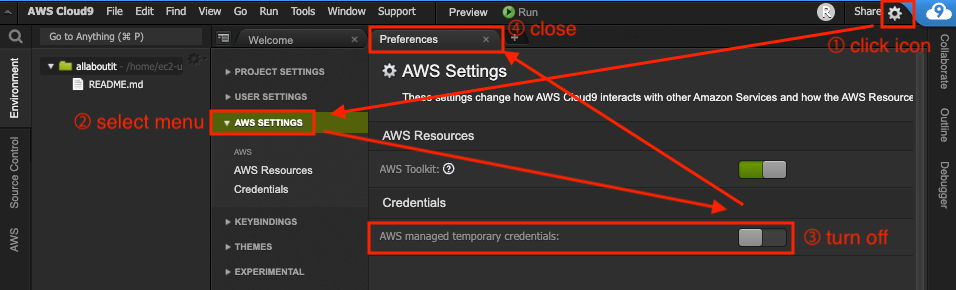
Remove existing credential files to ensure Temporary credentials are not present.
rm -vf ${HOME}/.aws/credentialsUse the GetCallerIdentity CLI command line to check that Cloud9 IDE is using the correct IAM Role. If the result value is shown it is set correctly.
aws sts get-caller-identity --query Arn | grep eksworkspace-admin
AWS CLI
Update AWS CLI
AWS Command Line Interface is an open source tool that can interact with AWS services using command-line shell commands. AWS Cloud9 has AWS CLI installed by default.
Cloud9 IDE has AWS CLI 1.x version installed by default. Use the command below to upgrade the AWS CLI version to 2.x.
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip" unzip awscliv2.zip sudo ./aws/install export PATH=/usr/local/bin:$PATH source ~/.bash_profileUse the command below to check the version. You must meet 2.x version.
aws --version
kubectl
Install kubectl
kubectl is the CLI that commands a Kubernetes cluster.
Kubernetes uses Kubernetes API to perform actions related to creating, modifying, or deleting objects. When you use the kubectl CLI, the command invokes the Kubernetes API to perform the associated actions.
Click here to install the corresponding kubectl to the Amazon EKS version you want to deploy. In this workshop, we will install the latest kubectl binary(as of April 2023).
sudo curl -o /usr/local/bin/kubectl \ https://s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/amazon-eks/1.26.2/2023-03-17/bin/linux/amd64/kubectlsudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/kubectl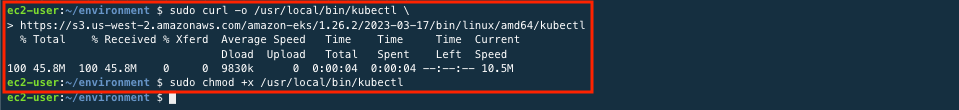
Use the command below to check that the latest kubectl is installed.
kubectl version --client=true --short=true
ETC
Install jq
jq is a command line utility that deals with data in JSON format. Using the command below, install jq.
sudo yum install -y jq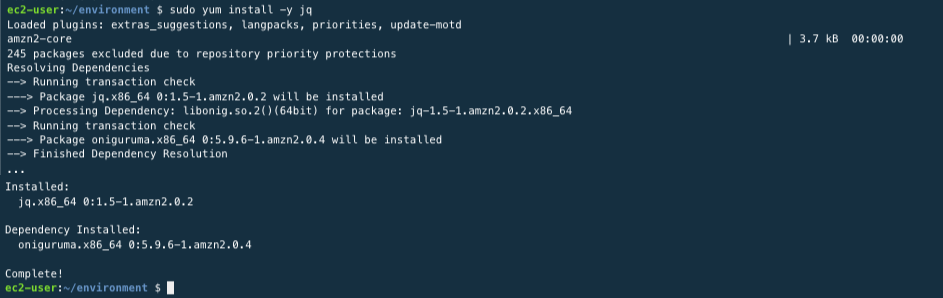
Install bash-completion
In the Bash shell, the kubectl completion script can be created using the kubectl completion bash command. Sourcing the completion script to the shell enables automatic completion of the kubectl command. However, because these completion scripts rely on bash-completion, you must install bash-completion through the command below.
sudo yum install -y bash-completion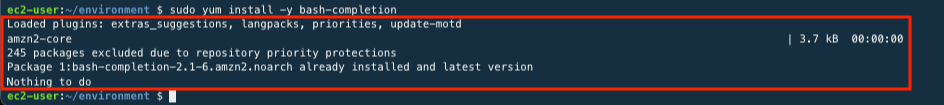
Install Git
Click the Git Downloader link and install the git.
sudo yum install gitgit --version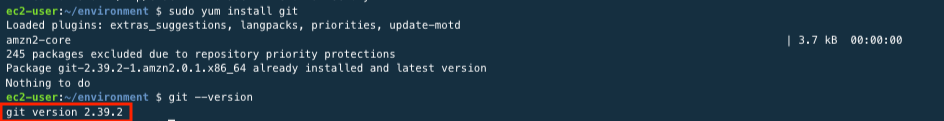
Install python because CDK for Python is used. Python is installed by default in the Cloud9 environment. Python Installer Select the appropriate package from the link to download and install it.
python --version python3 --version
Check PIP
Checks whether PIP, a manager that installs and manages Python packages, is installed. It is installed by default in certain versions of Python and above.
pip --version pip3 --versionIf not installed pip install page recommended to proceed with the installation according to the guide or install with the latest version of Python.
Install eksctl
There are various ways to deploy an Amazon EKS cluster. AWS console, CloudFormation, CDK, eksctl, and Terraform are examples. In this lab, we will deploy the cluster using eksctl.
eksctl is a CLI tool for easily creating and managing EKS clusters. It is written in Go language and deployed in CloudFormation form.
Download the latest eksctl binary using the command below.
curl --silent --location "<https://github.com/weaveworks/eksctl/releases/latest/download/eksctl_$(uname> -s)_amd64.tar.gz" | tar xz -C /tmpsudo mv -v /tmp/eksctl /usr/local/bin
sudo mv -v /tmp/eksctl /usr/local/bin
Use the command below to check the installation.
eksctl version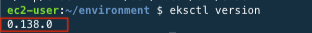
Install CDK
Install CDK to distribute resources to be used in the CI/CD part.
CDK is installed by default in the Cloud9 environment. Execute the command below to check whether the CDK is installed.
cdk --version
NPM needs to be installed to install the CDK.
NPM Installer Select the package suitable for your environment from the link, download and install it.
After installing NPM, execute the command below to install cdk.
npm install -g aws-cdkIf you see error messages like below.
This problem is from existing files that have already been installed. so, use –force for updating.
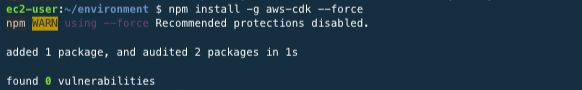
Check whether the cdk is properly installed.

AWS Cloud9 Additional Settings
On the previous chapter, we deploy AWS Cloud9 IDE and install the required tools, then proceed to the additional setup below.
Set default value to AWS Region that is currently using.
export AWS_REGION=$(curl -s 169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document | jq -r '.region') echo "export AWS_REGION=${AWS_REGION}" | tee -a ~/.bash_profile aws configure set default.region ${AWS_REGION}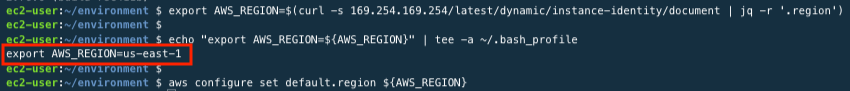
export AWS_REGION=$(curl -s 169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document jq -r ‘.region’): This command is a shell script that is executed within an AWS EC2 instance. It retrieves the region information of the current instance from the instance metadata service using the curl command and extracts the region information using jq. The extracted region information is then assigned to the AWS_REGION environment variable. echo “export AWS_REGION=${AWS_REGION}” tee -a ~/.bash_profile: This command adds an export statement to the .bash_profile file to permanently set the AWS_REGION environment variable. The statement is executed every time the shell is started to set the AWS_REGION environment variable. The tee -a option appends the output to the file. - aws configure set default.region ${AWS_REGION}: This command configures the AWS CLI using the aws configure command. It sets the default.region configuration to the AWS_REGION environment variable to use the instance’s region information as the default region. This allows for easier access to AWS resources without having to specify the region information every time an AWS CLI command is executed.
Check AWS region.
aws configure get default.region
Register the account ID you are currently working on as an environment variable.
export ACCOUNT_ID=$(curl -s 169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document | jq -r '.accountId') echo "export ACCOUNT_ID=${ACCOUNT_ID}" | tee -a ~/.bash_profile
If you do not set AWS Region, an error occurs when you deploy the cluster and check the relevant information.
During the docker image build, the AWS Cloud9 environment may experience a capacity shortage issue. To resolve this, run a shell script that extends the disk size.
wget <https://gist.githubusercontent.com/joozero/b48ee68e2174a4f1ead93aaf2b582090/raw/2dda79390a10328df66e5f6162846017c682bef5/resize.sh>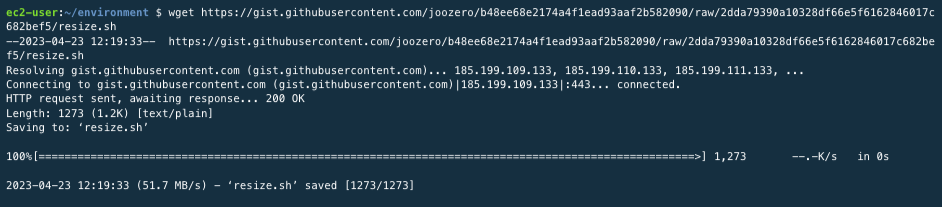
sh resize.sh
wget ‘https://gist.githubusercontent.com/joozero/b48ee68e2174a4f1ead93aaf2b582090/raw/2dda79390a10328df66e5f6162846017c682bef5/resize.sh’: This command uses the wget command to download the resize.sh script from GitHub Gist. This script uses ImageMagick to resize image files.
sh resize.sh: This command executes the downloaded resize.sh script. This script resizes all JPG image files in the current directory to 50% of their original size. The resized files are saved in a resized directory.
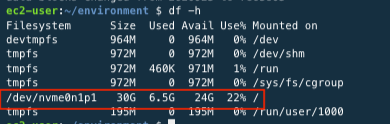
After completion, use the command below to check that the increased volume size is reflected in the file system.
df -h